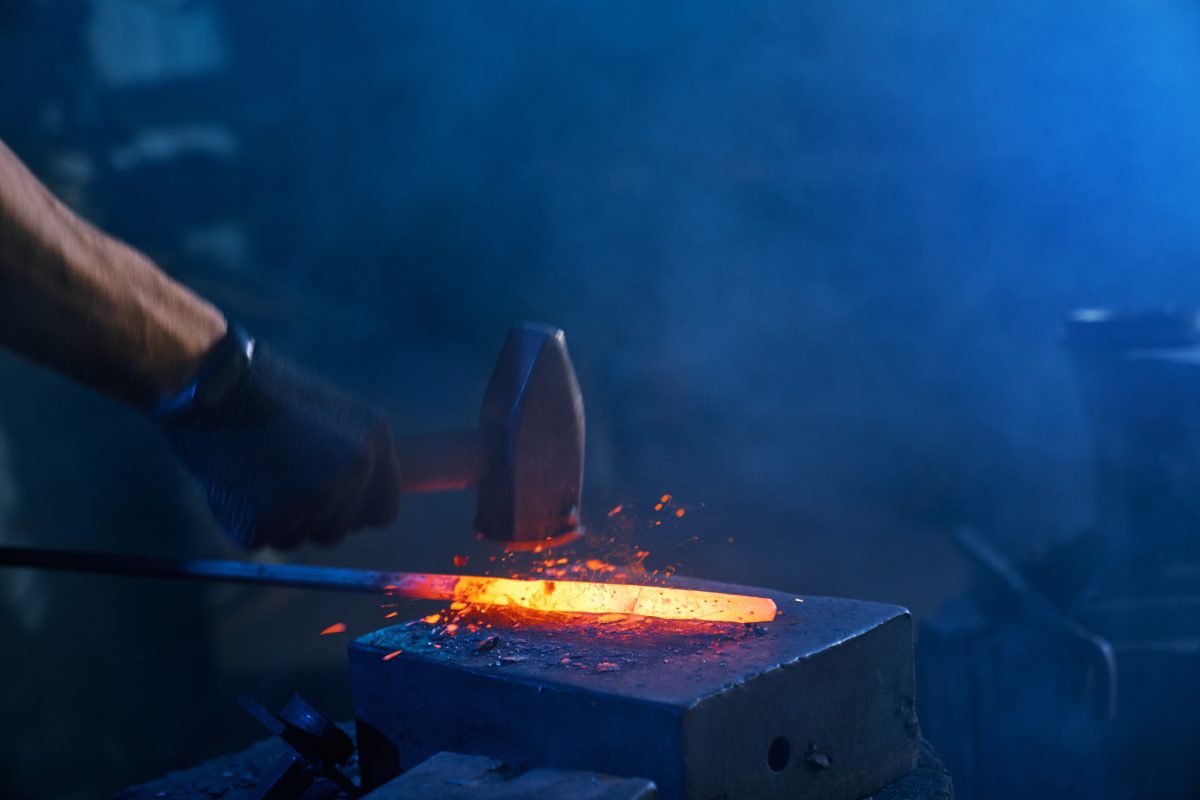
Forging, Explained…
In simple words, all we can say about the inception of forging is from “The Humble Beginnings to Modern Marvel” Forging is a metal functioning/shaping method that deforms, manipulates, or shapes metal to achieve a wanting form, configuration, or appearance which outlines by a metal processing design. It is usually categorized by the type of metal and the requirements of the design, whether it shall be completed using cold or hot forging processes.
Forging has been one of the ancient metalworking techniques for thousands of years. While forging remains the same, technological progress in metallurgy and engineering has made it a technical art form. Over generations, new technologies and processes have been developed, improving production times and increasing the strength and structural integrity of forged parts.
Did you know? A wide range of metals can also be forged just like typical metals which include carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel. Also, very soft metals like aluminum, copper, and brass can also be forged. It is usually categorized according to the temperature at which it is performed whether it is cold, warm, or hot forging. It might seem that forging is an ancient way procedure but it is still a crucial part for many metalworking manufacturers.
- Let’s understand how Forging is classified:
Basically, forging is classified into two wide types and there are sub-types classified under those. One is based on the Die Used and another one is based on the Workpiece temperature. Wherein in die used like open-die, close-die seamless ring forging are there and on the other hand in work piece temperature there are Hot Forging and Cold Forging.
However, if we try and understand there are various forging types which are mentioned below:
- Cold Forging
- Open Die Forging
- Drop Forging
- Closed Die Forging
- Hot Forging
- Impression Die Forging
- Roll Forging
- Warm Forging
- Press
- Isothermal Forging
- Automatic Hot Forging
- Metalsmith
- Hammer Forging
- Precision Forging
- Open Die Drop Forging
- Forge Welding
- Multi-Directional Forging
- Drop Forging Process
- Induction Forging
- Roll Forging Process
What do you think the purpose and uses of Forging would be ?
With the help of this blog, let’s understand the concrete purpose and usage of forging. In most basic sense, the metal parts are created through forging which is the primary purpose of forging. Metal forging generates more powerful manufacturing parts available as compared to other manufacturing methods. The more and more metal is pressed and heated, minor cracks are sealed which leads to any empty spaces in the metal close.
The forging process is highly multipurpose and can be used on small parts just a few inches in size to large components that weigh up to 700,000 lbs. It is used to produce critical aircraft parts and transportation equipment. Forging is also used to fortify hand tools such as chisels, rivets, screws, and bolts.